Текст
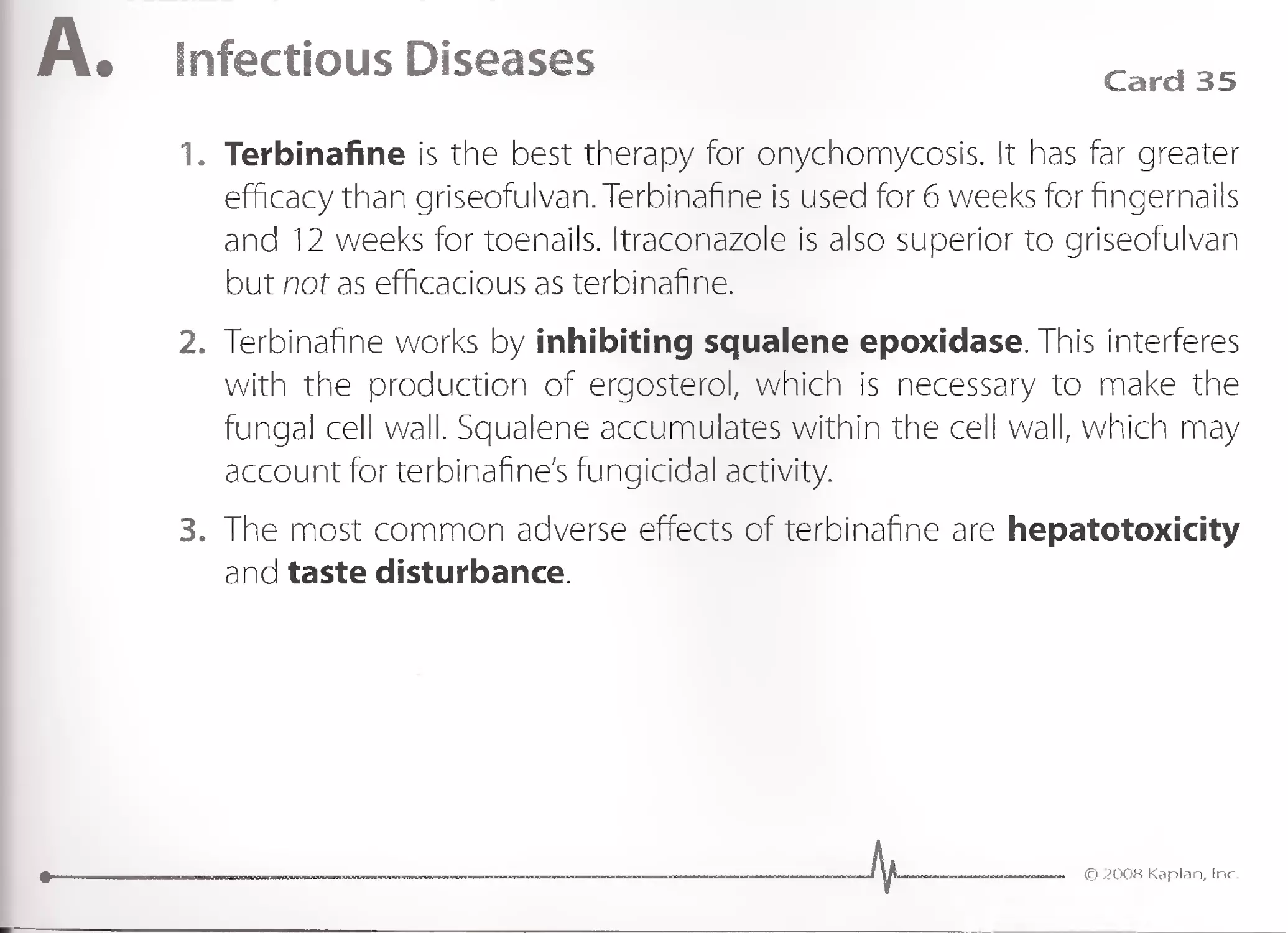
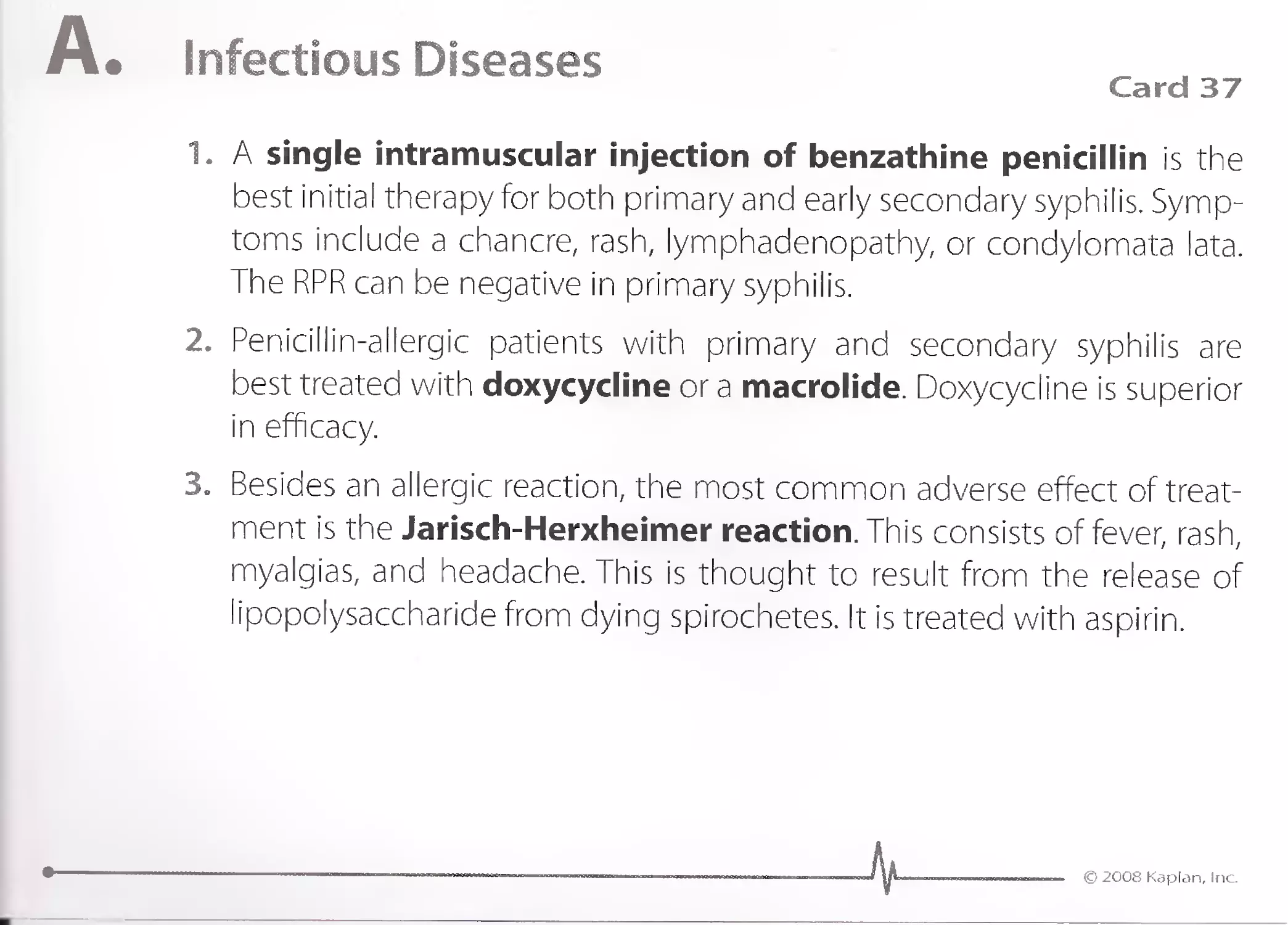
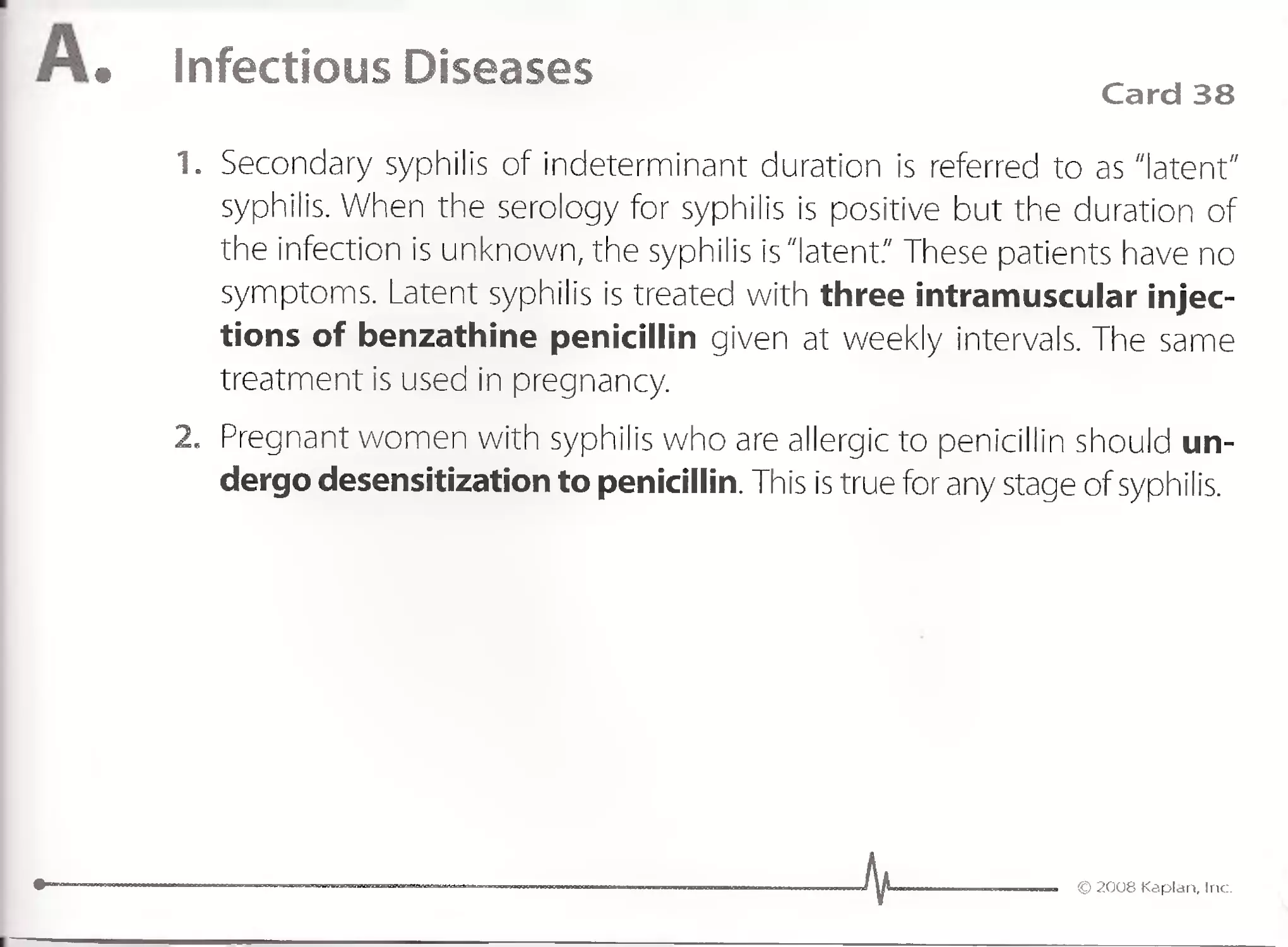
Q. Dermatology
Minocycline
.
Card 1
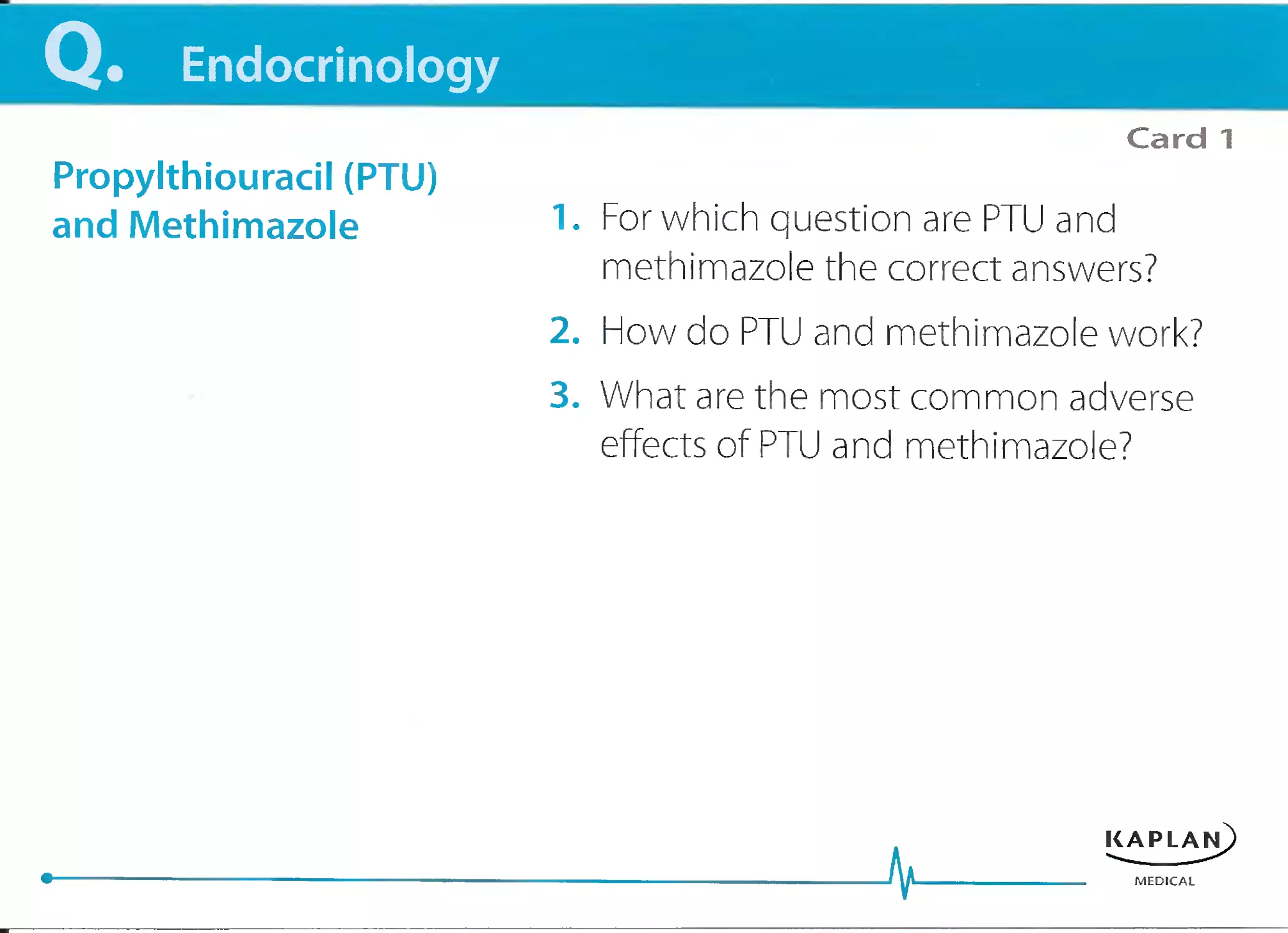
1. What is the most common question for
which minocycline is the answer?
2. How does minocycline work?
3. What are the most common adverse
effects of minocycline?
MEDICAL
A.
Dermatology
Ca rd 1
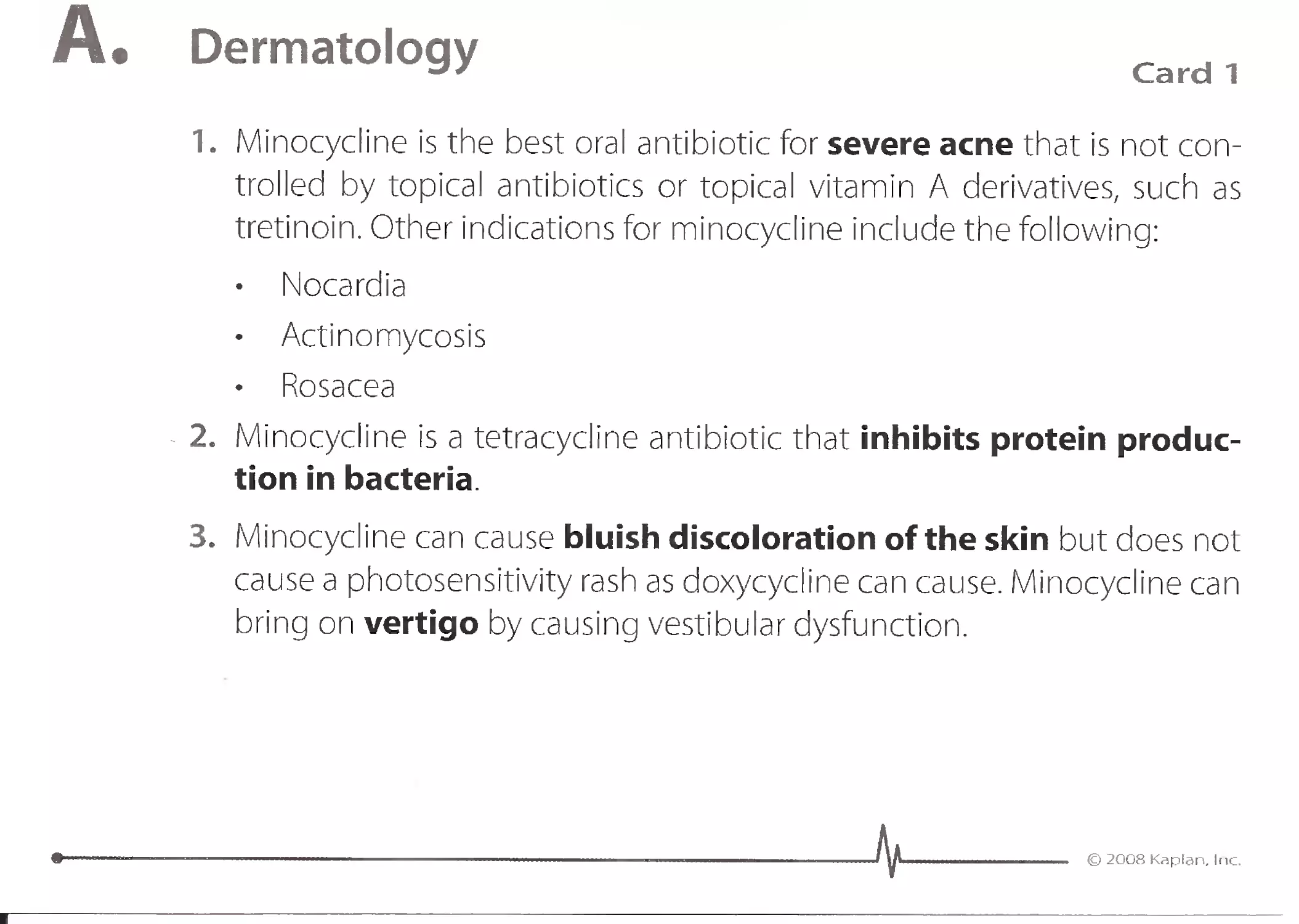
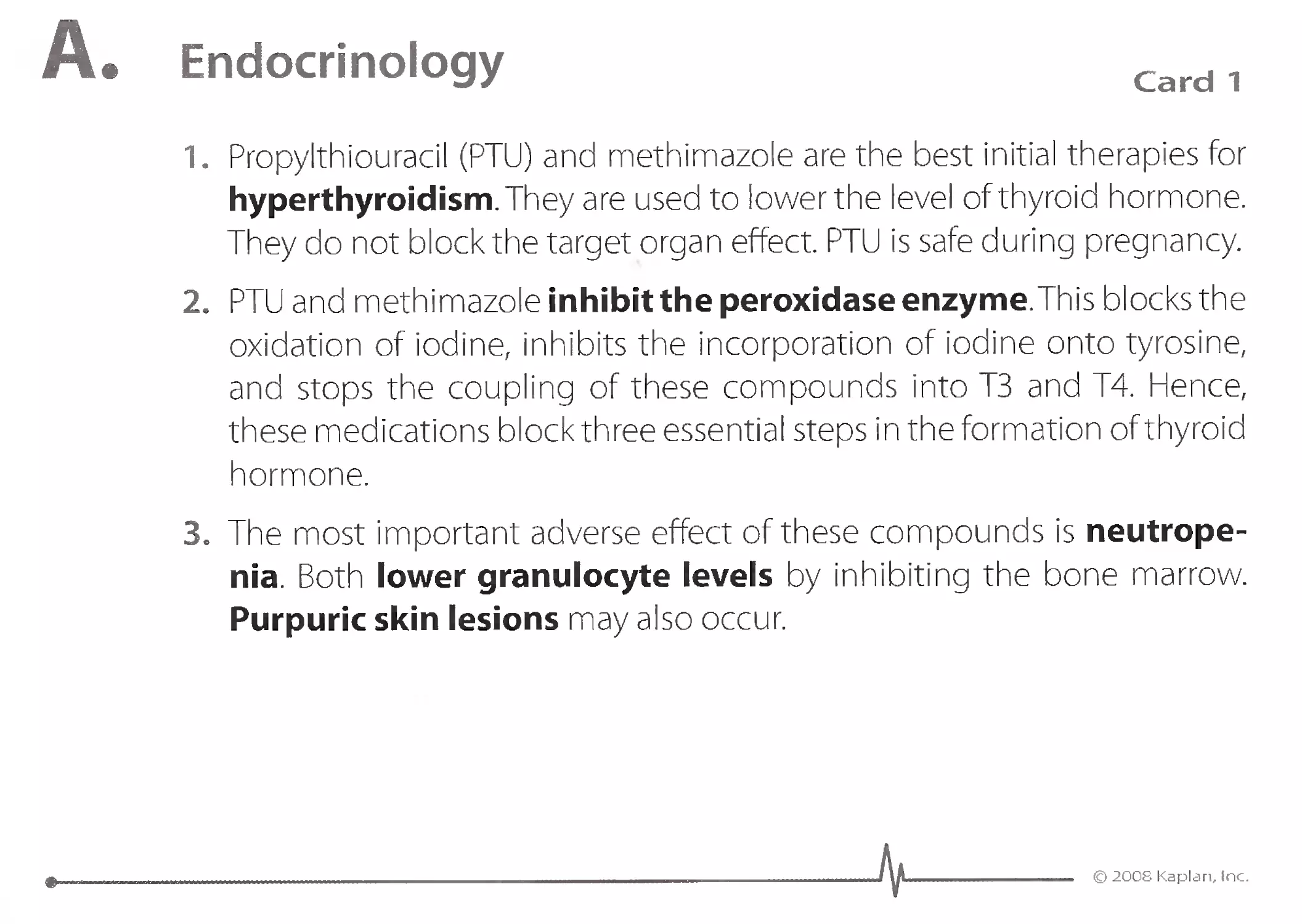
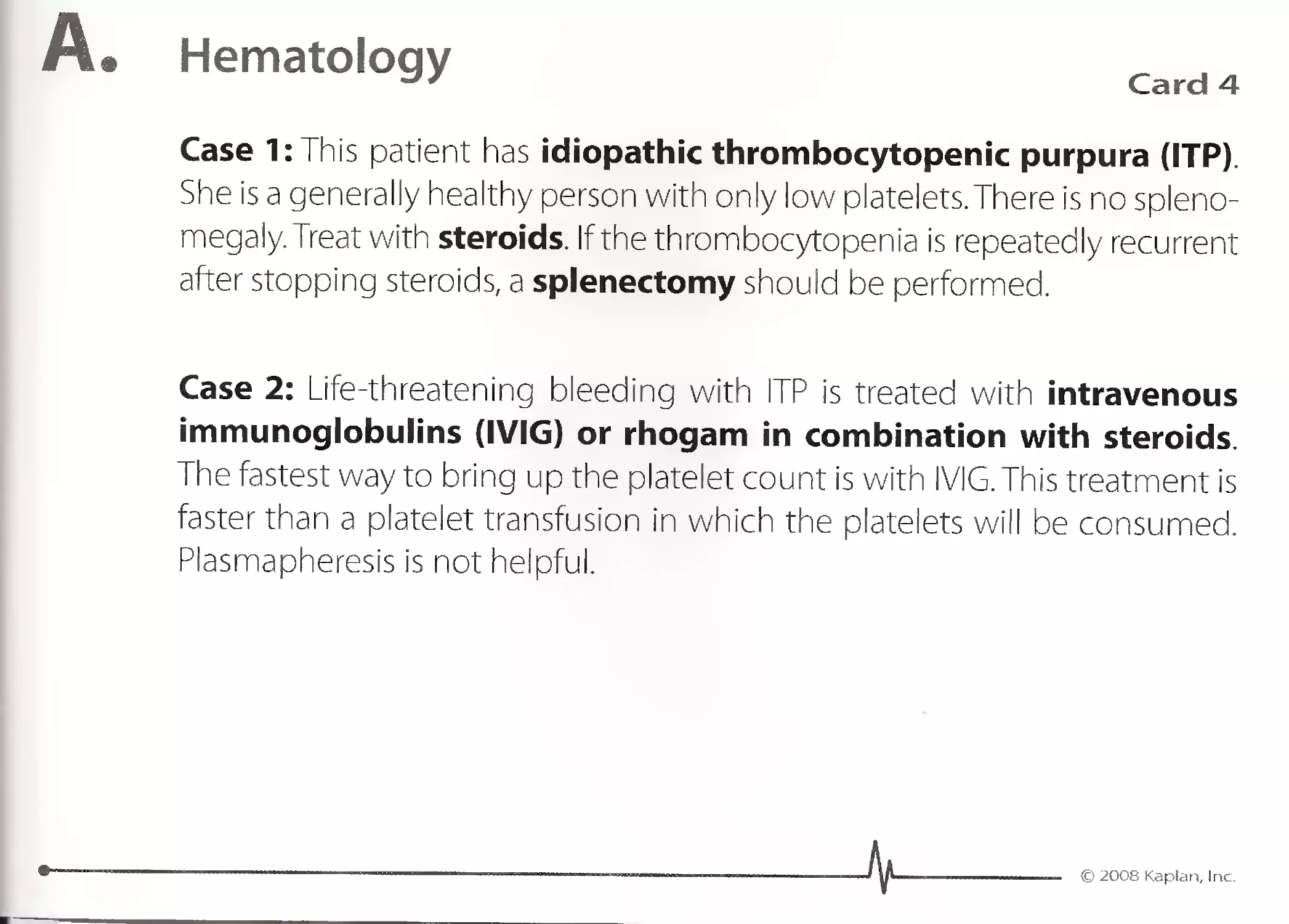
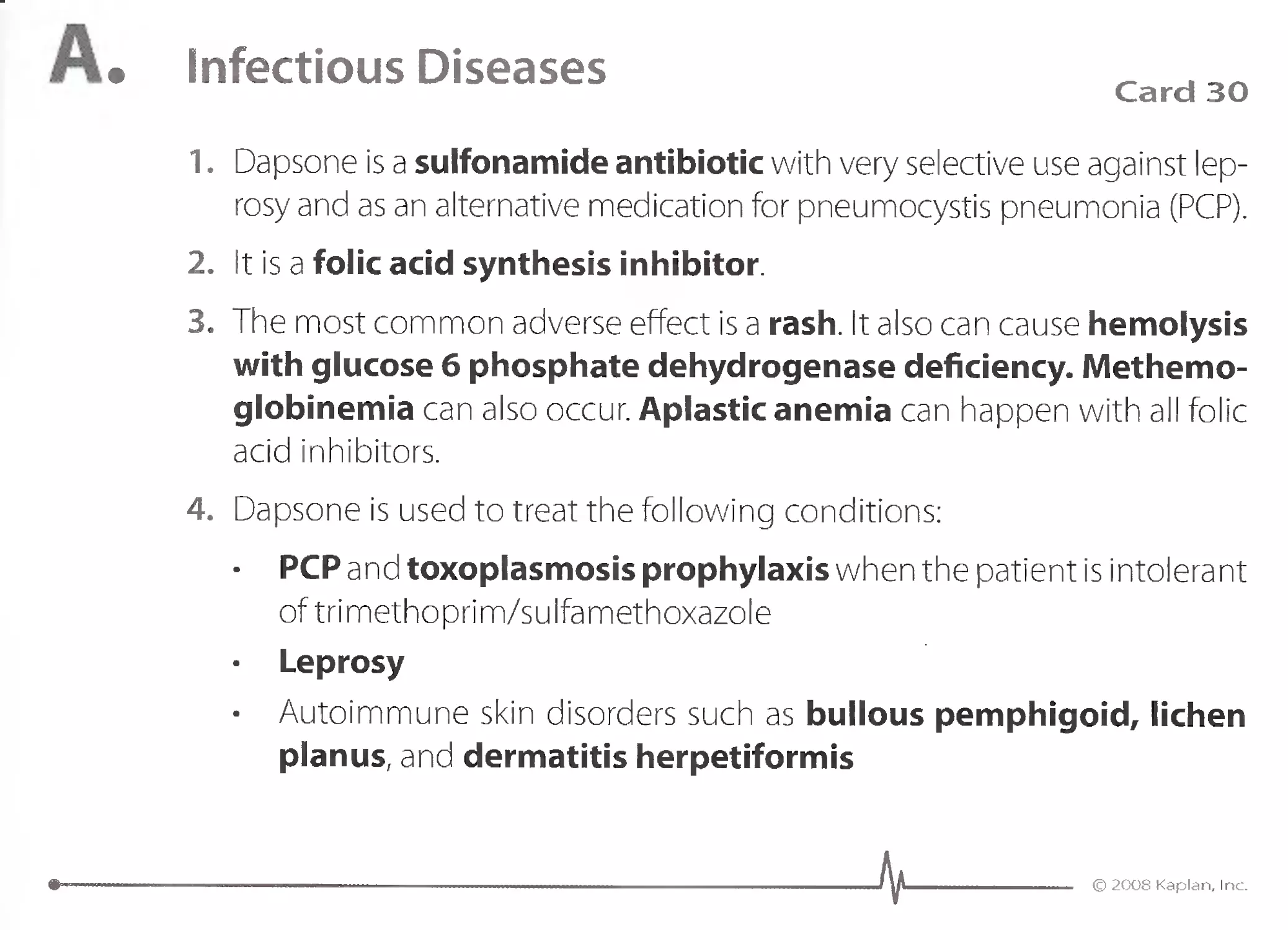
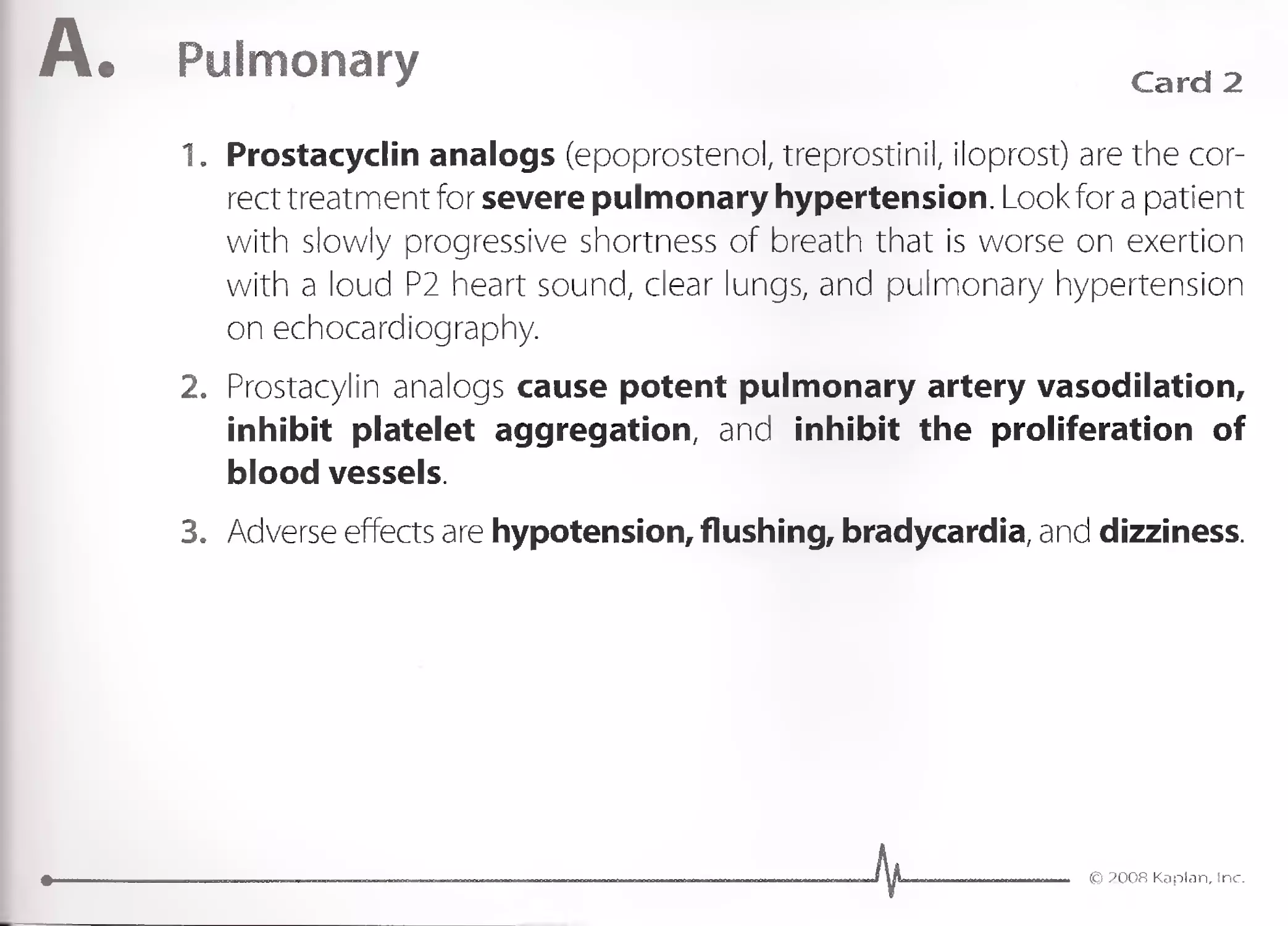
1. Minocycline is the best oral antibiotic for severe acne that is not con-
trolled by topical antibiotics or topical vitamin A derivatives, such as
tretinoin. Other indications for minocycline include the following:
Nocardia
Actinomycosis
Rosacea
'. 2. Minocycline is a tetracycline antibiotic that inhibits protein produc-
tion in bacteria.
3. Minocycline can cause bluish discoloration of the skin but does not
cause a photosensitivity rash as doxycycline can cause. Minocycline can
bring on vertigo by causing vestibular dysfunction.
.
@ 2008 KiJplan, IrIC.
.
Q. Dermatology
Case 1: A woman comes in
with mild acne. She has a few
comedones with an occasional
infiamed papule or pustule.
Case 2: A man has failed initial
therapy for acne and has nu-
merous papules and pustules
with mild scarring.
Case 3: Your patient is very
distressed and depressed be-
cause of numerous large cysts
on the face, neck, and trunk.
He is severely scarred.
.
.
Card 2
1. What is the treatment for each of these
cases?
2. How does each treatment work?
3. What are the adverse effects of these
treatments?
MEDICAL
.
Dermatology
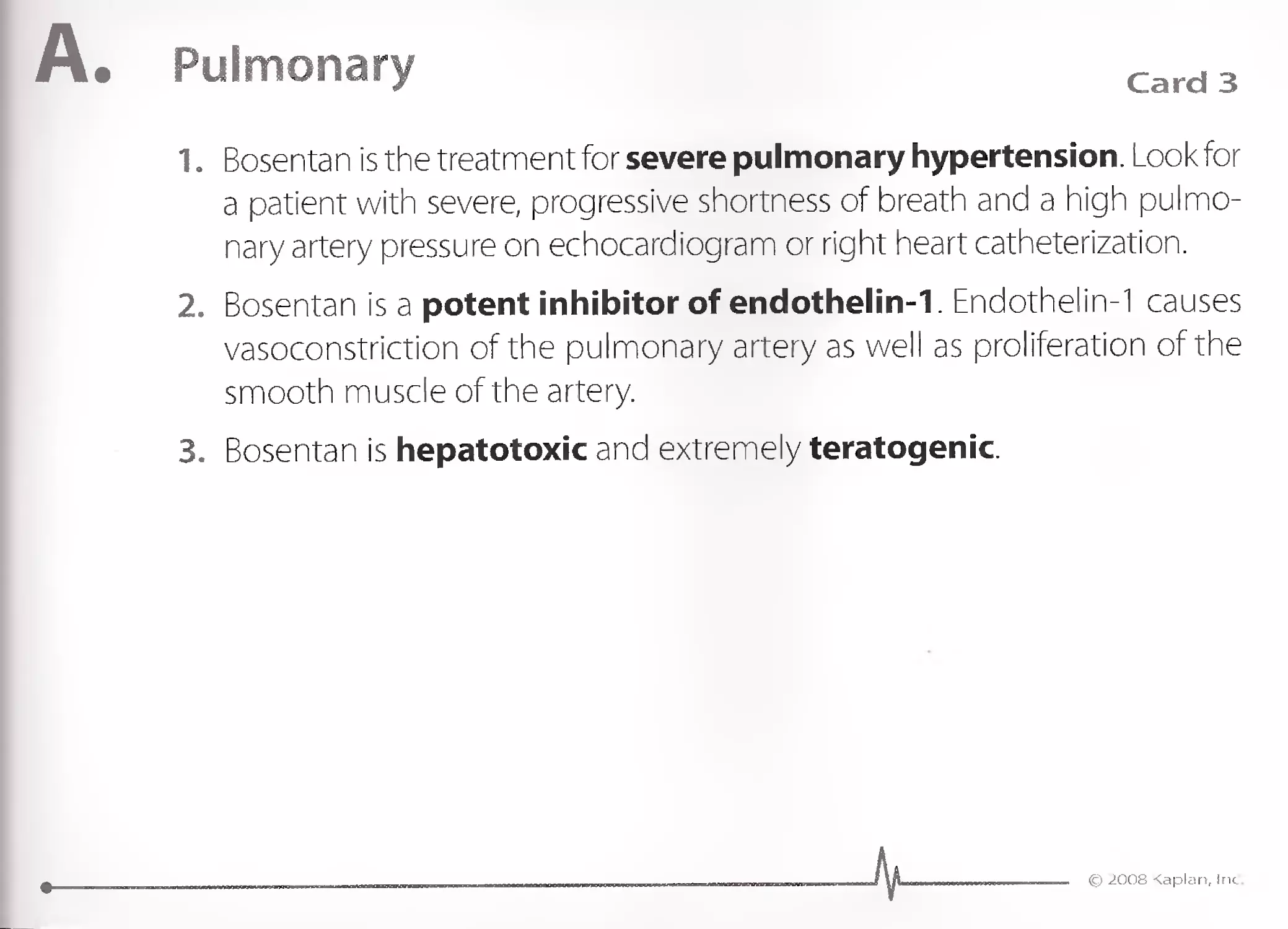
Ca rd 2
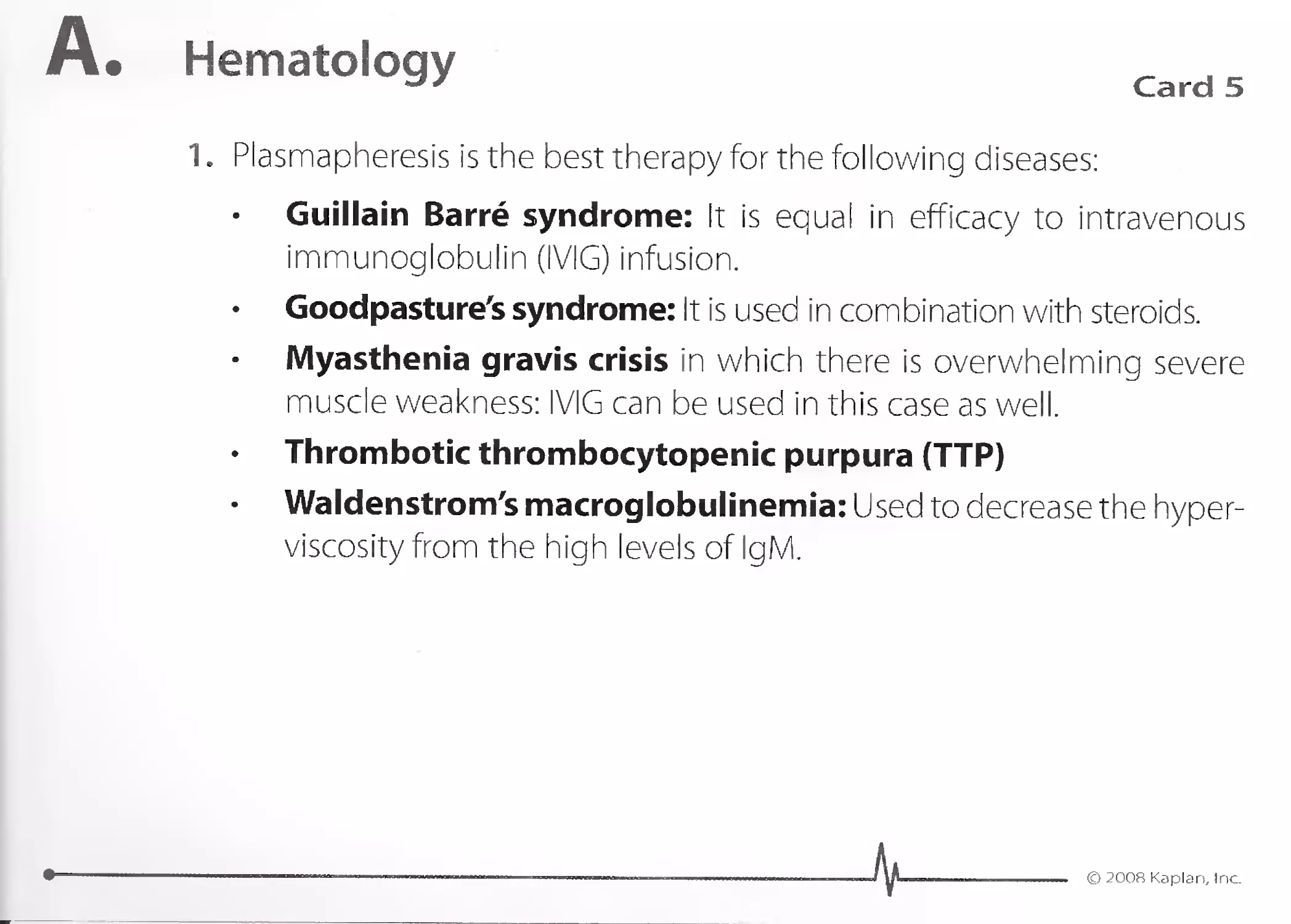
Case 1: is mild comedonal acne. Mild disease is treated with topical ben-
zoyl peroxide and a topical antibiotic, such as erythromycin or clin-
damycin. Benzoyl peroxide is both antibacterial and comedolytic. Topical
antibiotics will eliminate the causative organism Propionibacterium acnes
from the comedones.
Case 2: is moderate to severe acne resulting in scarring. In addition to
benzoyl peroxide, the patient should be treated with a topical vitamin
A derivative (tretinoin). An oral antibiotic, such as minocycline, should
be used.
Case 3: is severe cystic acne. An oral antibiotic and oral vitamin A
(isotretinoin) are needed. Isotretinoin will decrease sebum production but
is extremely teratogenic and can cause severe depression, dry skin,
and hyperlipidemia.
.
@ 2008 Kaplan, Inc.
Q. Dermatology
Case: An adolescent boy
comes to see you for treat-
ment of a long-standing itchy,
eczematous rash on his face,
hands, and feet in the fiexural
areas. The skin is lichenified
from scratching. He also has
seasonal rhinitis and occasional
urticaria.
.
Card 3
1. What is the best therapy to treat the
itching?
2. What is the best long-term therapy?
3. What are the other indications for this
therapy?
MEDICAL
A.
Dermatology
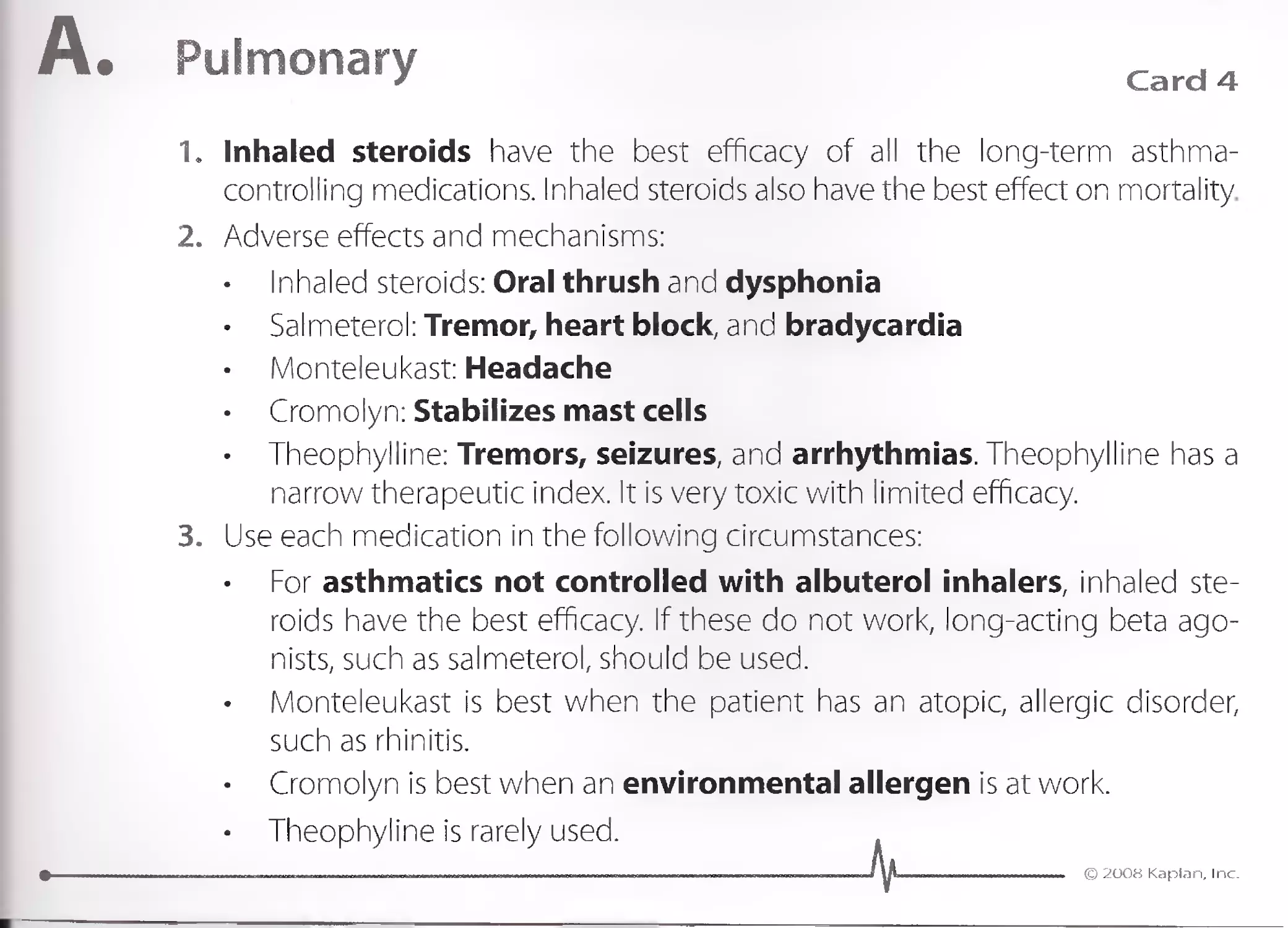
Card 3
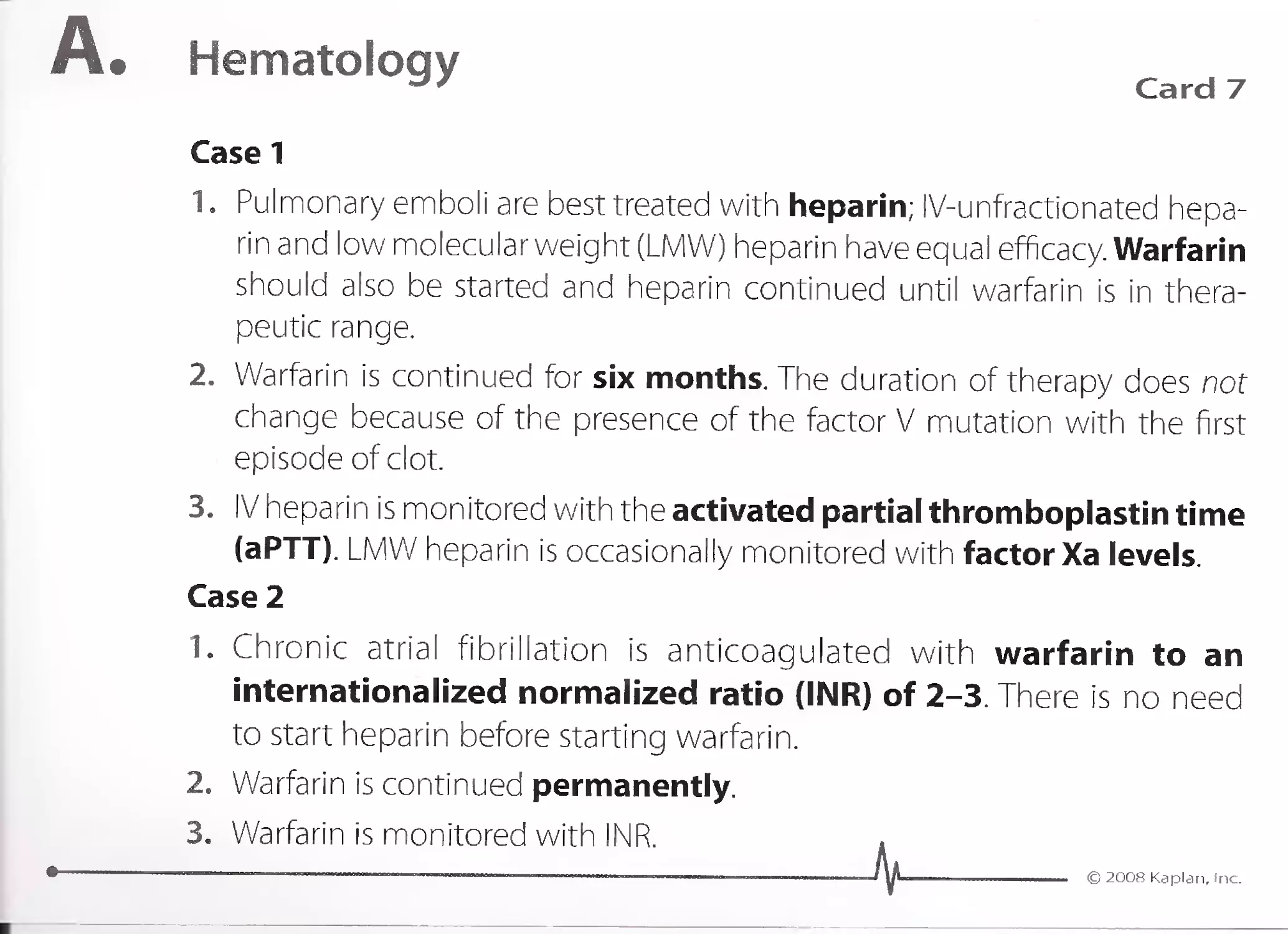
1. Atopic dermatitis is treated with antihistamines, such as fexofenadine,
cetirizine, or loratadine. Hydroxyzine and diphenhydramine are more
potent but much more sedating. Doxepine is a tricyclic with extensive
antihistamine effects.
2. Atopic dermatitis sym ptoms ca n be lessened in the long term by moistur-
izing the skin, avoiding harsh soaps, a nd treating skin infections.
Although topical steroids are effective to control symptoms acutely, in
the long term, they lead to skin atrophy. Topical calcineurin inhibitors,
such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, can control atopic dermatitis
in the long term without using steroids.
3. Antihistamines, such as fexofenadine, are also used for the following
conditions:
Allergic/seasonal rhinitis
Angioedema
Urticaria
.
«J 2008 Kaplan, irK.
Q. Dermatology
Case: A woman comes to the
office for pruritic, silvery, scaly
lesions of the knees, el bows,
and hands. The lesions are on
the extensor surfaces.
.
Card 4
1. What is the best therapy for localized
disease of this type?
2. What is the best therapy for extensive
disease of this type?
MEDICAL
.
Dermatology
Card 4
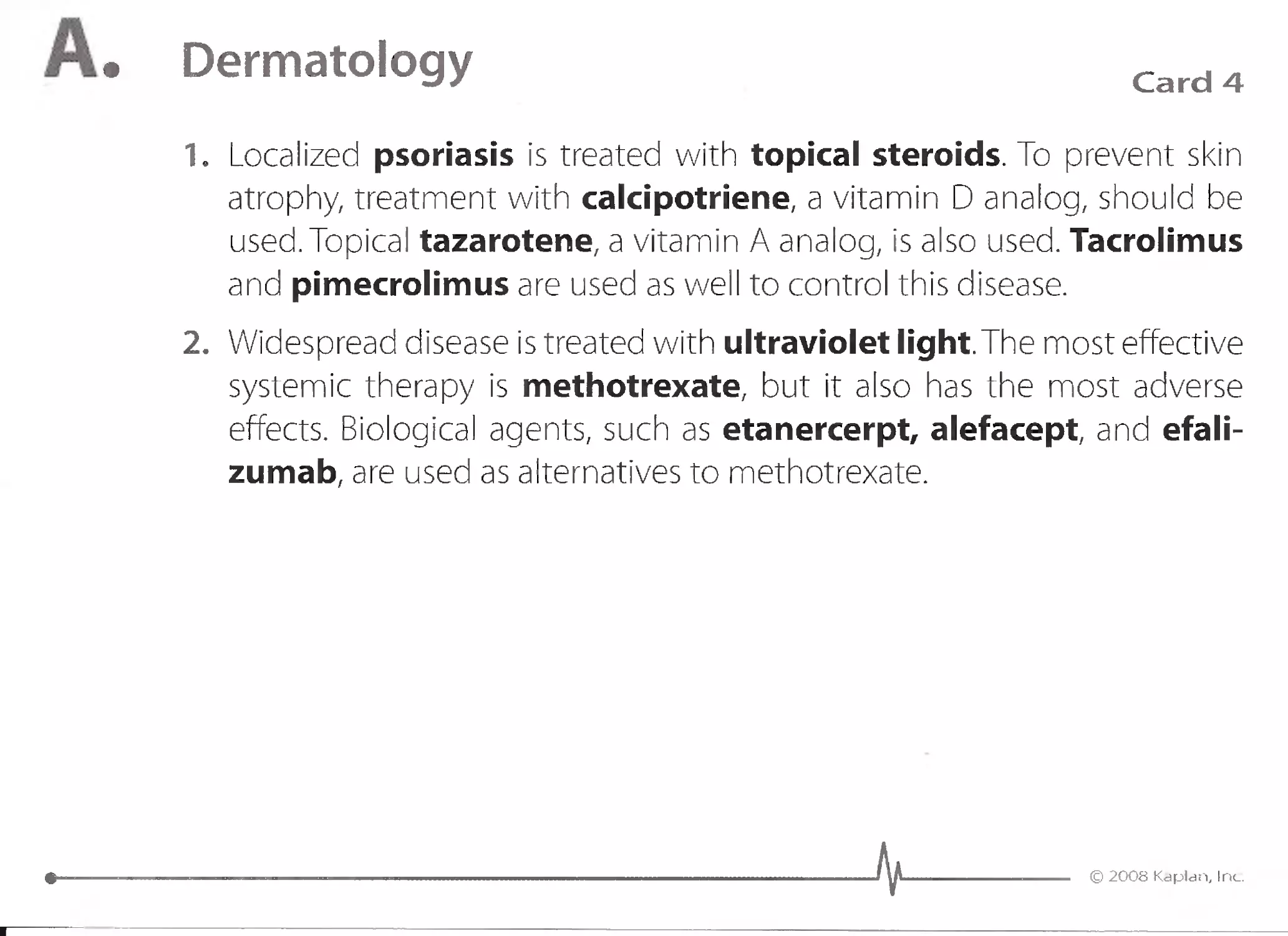
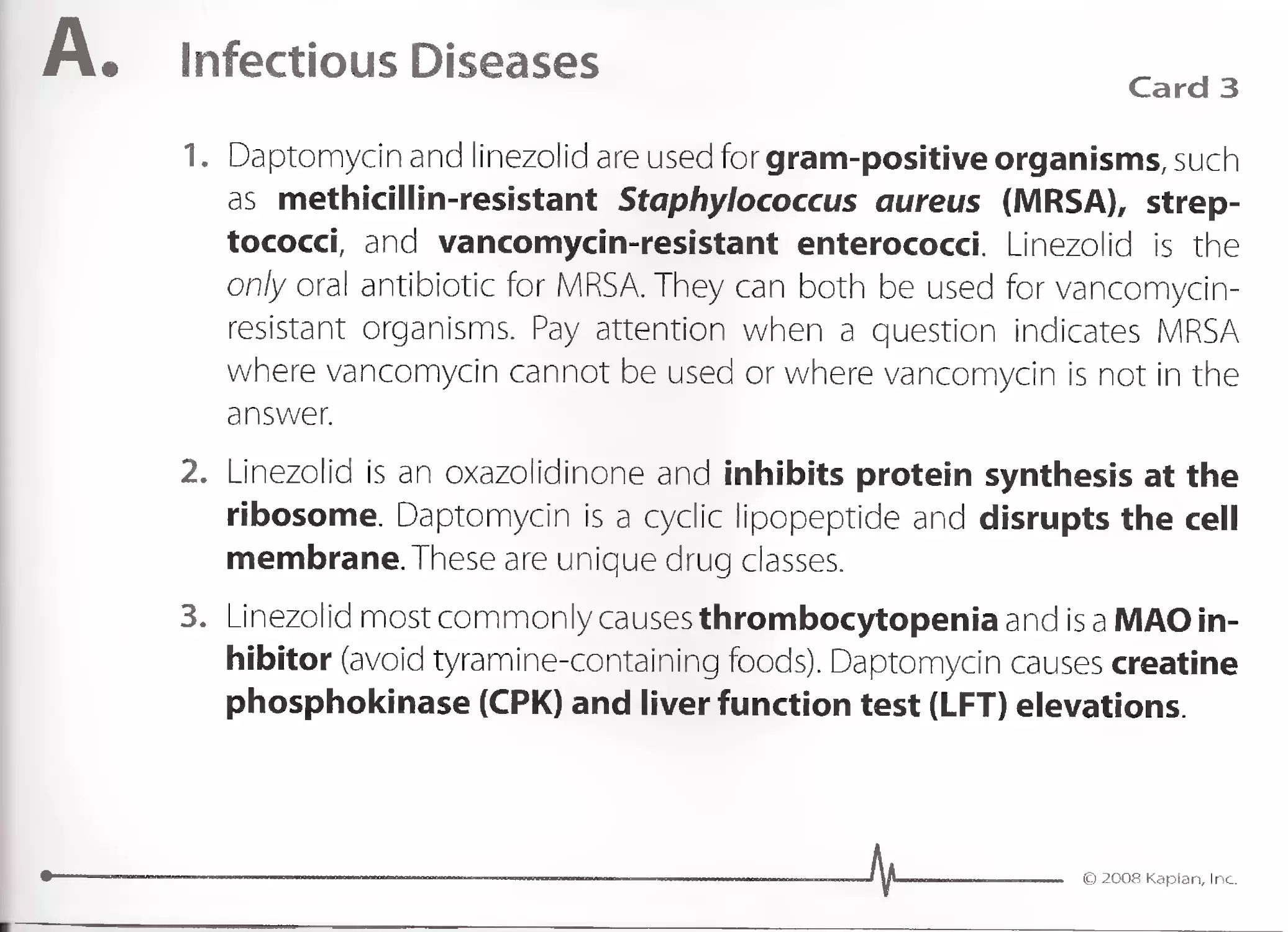
1. Localized psoriasis is treated with topical steroids. To prevent skin
atrophy, treatment with calcipotriene, a vitamin 0 analog, should be
used. Topical tazarotene, a vitamin A analog, is also used. Tacrolimus
and pimecrolimus are used as well to control this disease.
2. Widespread disease is treated with ultraviolet light. The most effective
systemic therapy is methotrexate, but it also has the most adverse
effects. Biological agents, such as etanercerpt, alefacept, and efali-
zumab, are used as alternatives to methotrexate.
.
@ 2008 Kdpldn, Inc.